
Fish oil. Sounds disgusting, does it not? Oh, there is nothing wrong with fish in particular, but we all know about that “fishy taste,” and aren’t oils the reason we get pimples?
You get the point.
Fortunately, the reality of fish oil is considerably different from the term itself. And by now, you probably have enough people in the family taking it to be aware of some of its key benefits.
In the following article, we will be unpacking fish oil in all its grandeur. We will discuss the primary use. We will cover what makes it such a preferred substance for the health-conscious.
And in addition to its known and ancillary benefits, we will be discussing some of the concerns that are associated with it. Let’s begin!

How Do People Use Fish Oil?
Visit any supplement producer’s website, and they will pitch fish oil as the be-all/end-all. A magical elixir of life!
While it is never a bad idea to have your guard up when it comes to health products, fish oil is one of the few that have actually received approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for assistance in lowering high triglycerides.
Triglyceride might be a nicer-sounding word, but it is also one of the main building blocks of natural fats and oils. Elevated concentrations in your blood test could mean that you run a higher risk of having a stroke.
Your doctor can detect whether the level of your triglycerides is too high by conducting a “lipid panel” test. Current American Heart Association guidelines recommend getting a lipid panel done every five years.
If you have triglyceride problems, your doctor will probably want to step that up a bit.
The “normal” level of your triglycerides should be less than 150 mg/dL. You are considered “borderline” if you come in between 150-199. Over 200 is “too high.” Over 500, and you are probably on borrowed time if you do not do something to correct it in a hurry.
Fortunately, there are options at your disposal.
For starters, you can stop consuming so many saturated fats (and definitely trans-fats). If you are not on an app that monitors your macronutrients, you should start doing that right away.
Collecting and analyzing your personal data will go a long way in helping you take control.
Secondly, use more olive oil or canola oil when cooking. These are high in the healthier mono and polyunsaturated fats. Also, you will want to eat more fruits and veggies and choose low- to no-fat options when consuming dairy.
Five other helpful factors include the following:
- Eating 25-30g of fiber per day.
- Limiting dietary cholesterol to 200mg per day.
- Moderating your alcohol consumption.
- Avoiding anything with refined or added sugars.
The last one — and the one on which the crux of this article rests — is fish intake. Eating fish as a main protein source 1-2 times per week will provide access to omega-3 fatty acids, which are the primary agents in being able to lower triglyceride levels.
Cold water fish like salmon are among the best sources. Word of warning, though: you might think the higher up the food chain you go, the better it gets; but that is not necessarily true.
Fish like shark, swordfish, albacore tuna, and tilefish, may indeed have higher omega-3 amounts, but they’re also packing a higher quantity of toxins such as cancer-linked mercury.
That’s why many supplement manufacturers derive their fish oil products from smaller species.
Now that we know why people use fish oil (primarily anyway), let’s look at what’s actually in it, and what other ways it could promote good health.

Fish oil primarily is known for its large quantities of Omega-3 fatty acids that it contains. Omega-3s have become more popular among health-conscious food producers as well.
What Is It’s Nutritional Profile?
Fish oil has become such a popular product on the nutritional supplement scene because it contains liberal supplies of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, or LCPUFAs, of the Omega-3 type. (Remember in the last section when we said less saturated/trans fat, more polyunsaturated in your diet!)
The two most popular that are found in fish oils include eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. We hope you’ll forgive us for refusing to write those out for the remainder of the article.
Instead we’ll call them what everyone else does — EPA and DHA.
What Is EPA?
EPA resides in the skin of cold water fish. These include the herring, tuna, cod liver, halibut, salmon, mackerel, and whale/seal blubber. Doctors use it on women at risk of eclampsia during their pregnancies.
The acid can be useful in this case because it helps regulate blood pressure. Other cases tied to the use of EPA include the following:
- Schizophrenia
- Heart disease
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Alzheimer’s
- Cystic fibrosis
- Age-related macular degeneration
We’ll delve further into how it, and fish oil in particular, might benefit these groups of patients in the next section. But first:
What Is DHA?
Many people will group in DHA with EPA as if they are basically the same thing, but that is not the case. Far from it, actually. DHA is its own unique animal.
Fish do not naturally produce fish oil in large enough quantities to be beneficial when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids, but they do consume other fish that contain it as well as microalgae or plankton.
That’s where DHA comes in. It’s primarily transmitted through the algae part of the diet. And as far as its major health benefit is concerned, the brain gets the most bang-for-buck.
In fact, pregnant women often consume DHA to help with the mental development of their children, and it is used for the same purpose with premies.
Among the subtopics in the next section (other positive health benefits of taking fish oil), we’ll be talking about how DHA also can be of use to adults.
What Are the Positive Health Benefits?
Beyond triglycerides and brain development in the very young, fish oil has been put to good use in a number of other areas. Let’s look at each one in more depth.
Targeting Joint Health
One of the many issues you won’t be fond of as you get older is the damage time does to your joints. Simple acts like getting on the ground to play with your kids or grandkids and then getting up afterward (or trying to) just don’t come as easily as they used to.
We can’t tell you that all fish oil supplements will help address this — after all, there are additive ingredients and the EPA/DHA content differs — but what we can tell you is a number of supplements are specially formulated to address areas of concern such as tenderness, morning stiffness, swelling, and discomfort.
And if you’re Old School Charles Bronson tough and think you’ll just “live with it,” keep in mind that poor joint health can influence your activity levels, as in, make you not want to work out or stay in shape.
The less active you are with age, the more other health concerns can, and will, arise.
Healthline adds that many are starting to use fish oil as a helpmate in the treatment of arthritis. This is likely because the EPA/DHA content are anti-inflammatory agents.
Working to De-Flame Cells
Chronic inflammation, notes a 2012 study from the University of California-San Diego, is a major contributor to almost every deadly disease (cancer, diabetes, etc.). Fish oil can act to help address these issues.
In the study, “the scientists stimulated (lab mice) to produce an inflammatory response. They discovered that omega-3 fatty acids inhibit an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX), which produces the prostaglandin hormones that spark inflammation.
The action is similar to what happens when one takes an aspirin, which disrupts the COX-2 signaling pathway, thus reducing inflammation and pain.”
Of course, that doesn’t mean omega-3s are going to cure cancer or fix everything wrong with you, but less inflammation can improve whatever condition you are experiencing, and make for a better quality of life.
Addressing the Nervous System
According to research published by the American Psychological Association in 2009, the two omega-3s found in fish oil could be useful to the body’s nervous system.
Norman Salem Jr., PhD, leader of the study at the Laboratory of Membrane Biochemistry and Biophysics at the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, joined with a team of researchers on the project.
The methodology was to feed “four different diets with no or varying types and amounts of omega-3s to four groups of pregnant mice and then their offspring,” the APA site notes, adding that the team measured offspring responses, once grown, to “a classic test of nervous-system function in which healthy animals are exposed to a sudden loud noise.”
Animals in such situations tend to flinch or show some other form of instinctive response. But “when they hear a softer tone in advance, they flinch much less,” the report stated.
This “warning” mechanism acts to prepare the organism for future stimuli. But in this case, only the mice that had received sufficient DHA/EPA amounts, not their precursor of α-linolenic acid (LNA), demonstrated “normal” gating when responding to a loud stimulant following a softer one.
The report continued: “The mice in all other groups, when warned, were startled nearly as much by the loud sound. When DHA was deficient, the nervous system most obviously did not downshift.
That resulted in an abnormal state that could leave animals perpetually startled and easily overwhelmed by sensory stimuli.”
The conclusion of the study was that even slight deviations from an adequate amount of DHA can produce negative brain effects.
Fish oil in the appropriate amounts may help improve the two factors tested here: alertness and adaptability.
Still not done with the brain, though, because, going back to the DHA, it also may work in…
Bettering Cognitive Function
We already know DHA is used by pregnant and nursing mothers in an effort to foster strong mental development for their children. But there also have been some studies to suggest similar benefits for adults, particularly those dealing with cognitive issues.
Now let’s be clear. Fish oil is not powerful enough to cure serious cognitive decline, such as that found in Alzheimer’s patients, or individuals suffering from schizophrenia.
However, many in the early stages of these diseases have found it useful in dealing with some of the effects.
That said, if there is a long-term benefit, it may be more useful to think of it as a preventative agent as fish oils for these purposes past a certain age could be too little, too late. WebMD does list fish oil as “possibly effective” for depression when used alongside conventional antidepressants like Citalopram.
Addressing Some Cardiovascular Issues
As mentioned earlier, fish oil is a known agent in the fight for better triglyceride levels. Therefore, it isn’t a stretch to think it could help in some other ways as well.
As WebMD notes, “taking EPA can reduce the risk of having a heart attack or other major event by up to 19%” for some suffering with coronary artery disease.
As far as any in-depth clinical studies to prove it one way or the other, the jury is still out. But just taking the triglyceride example, there are some ancillary benefits that can come with taking the right fish oil supplement.
Lower triglycerides means less fats in the blood stream. This can influence cholesterol, improving blood flow and helping you to feel more active in your day-to-day life.
Increased activity levels will always have heart-positive benefits. That said, you also want to make diet a part of the equation as well.
Other ‘Possibly Effective’ Uses
While the evidence is not as sound at this time, fish oil has been linked as “possibly effective” in addressing a few other conditions by the PDR for Nutritional Supplements.
Some of these include the following:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Lupus
- Asthma
Studies are ongoing as to the true effects, but it’s worth keeping your eye on if you suffer from any of these conditions.

Fish oil supplements like Nordic Oil (pictured here) are increasingly popular, both online, in supermarkets, and health stores.
What Should You Watch for When Picking a Supplement?
There are a lot of choices in the fish oil supplement arena, and to go through each one would not be productive. That’s because you never know who will still be around in the next year or two, or whether a recommended brand would upgrade their formula, thus negating the pick.
Also, it’s a $1 billion per year industry, so it would be tough to go through each one.
A more productive exercise is to tell you what to watch for when selecting one. Here are some of the high points as well as the warning signs.
Mercury Levels
Overexposure to mercury has harmful effects on the digestive, immune, and nervous systems. The heart, the kidneys, the brain, lungs — pretty much every organ that you need to survive can be adversely affected.
The toxic form of mercury is referred to as methylmercury. Fish, shellfish and fish-eating animals are carriers. The BBC put together a helpful guide to which fish are the biggest carriers (see below).
Basically, if the fish oil supplement is harvested from sources such as cod, salmon, or mackerel, it’s going to contain less mercurial content than the larger predatory fish (i.e., swordfish, tuna, etc.).
Just what’s the worst that can happen if you experience mercury poisoning?
- Vision Problems: Impaired peripheral vision is a common side effect. In addition to being uncomfortable and concerning, it can create life-threatening situations while operating heavy machinery, particularly an automobile.
- Sensory Issues: You know that horribly uncomfortable stabbing pain that your feet and hands start to feel whenever they’re “waking up” from having fallen asleep? That’s another symptom of mercury poisoning.
- Coordination Problems: Loss of hand-eye coordination has further-reaching effects than just messing up your video game play. If you do a job where your physical performance is important, then mercury poisoning can put you and others at risk.
- Difficulties with Communication and Mobility: Some people have reported slurred speech, problems hearing, and trouble walking when in-state.
- Muscle weakness: If you are concerned that you may have experienced mercury poisoning, but aren’t sure, you might consider stealing a page from Frank Costanza’s book and tackling a feat of strength that you ordinarily would be able to accomplish. If you are unable to do it or feel weaker than normal, it can be a concern.
Contaminated Fish Oil Supplements
When a fish oil supplement gets contaminated, it’s generally because of improper storage. Make sure that you follow the instructions on the label. Don’t leave refrigerated fish oils out overnight.
Don’t take them past the expiration date. In either case, the supplement might have spoiled and developed peroxides, which can irritate the eyes and skin or, in more severe cases, cause burns.
The level of contamination is generally dependent on the types of materials that were used in formulating the product.
Inaccurate Claims on EPA/DHA Content
Unfortunately, you can’t always take a supplement manufacturer at their word, so you will want to try different products to see which ones make you feel the best. The major area of concern is in the amount of EPA and DHA that are actually in the product.
Some fish oil supplements claim higher; others claim lower. In either case, they could be inaccurate with actual content for the higher claims lower than expected and for the lower claims higher than expected.
ConsumerLabs.com did a study in 2010 on the inaccurate readings that are out there on some of the packaging. Follow the link for the full findings, but here are a couple of noteworthy highlights:
- The cost to obtain 100 mg of EPA and/or DHA from fish oil ranged from about 1 cent to 15 cents for fish oil products, 30 cents from krill/algae oils. “A fairly standard daily dose of 500 mg of EPA + DHA from a quality-approved product could be had for as little as 6 cents. Higher prices were not associated with higher quality,” the study concluded.
- EPA/DHA ranged from lower than 20 percent to just over 80 percent of the advertised marine oil content seen on front labels. Consumers should defer to the side labels of products for a more accurate reading.
Tod Cooperman, M.D., ConsumerLab.com’s president, acknowledged the usefulness of fish oil, but cautioned consumers to be mindful of the differences and beware of the differences in quality, composition, odor-reduction, and price.
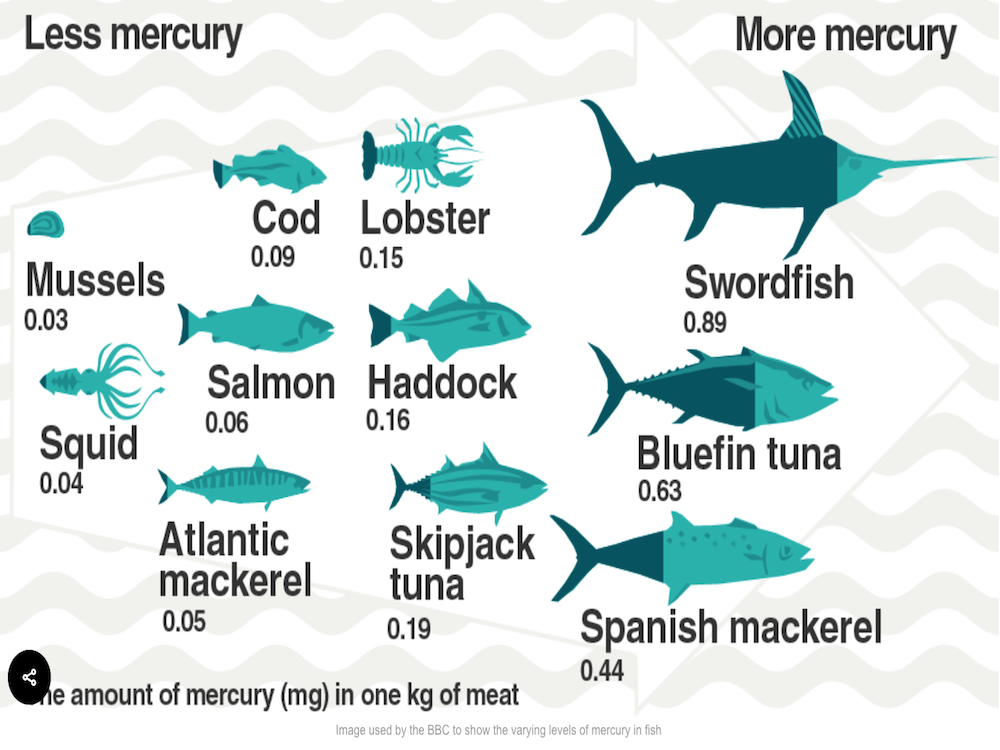
Mercury and other contaminants like dioxin and PCBs have been linked to cancer, but most fish contain it in very small amounts, making it less of a worry when it comes to fish oil. The main concern is that low-mercury sources are used.
Unpleasant Side Effects
It’s always popular that you might be perceived as rude when taking fish oil because it does bring with it a certain amount of side effects. For starters, you don’t want to take more than the recommended dosage.
Three milligrams per day in combined EPA/DHA is the recommended, and you should get no more than 2mg from a supplement, so don’t forget to work some actual fish into your diet during the week.
As far as unpleasant side effects go, you could experience loose stools, nausea. Some have even reported one-time blood-in-stool. You also may be subject to more nosebleeds as fish oil can act as a thinning agent.
Heartburn also is not uncommon, nor is skin irritation. Last but not least, there are the social faux pas: belching and bad breath, particularly.
In Closing
So there you have it, readers. Now that we’ve covered the uses, the potential benefits, the supplements, and the concerns related to fish oil, let’s hear from you. Do you use a supplement?
Have you been pleased with its effects? If so, what do you think the best source is: through your daily diet or a supplement product? Sound off in the comments section below.





Leave a Reply